Motion Compensation in Radiotherapy
Project Description
In radiosurgery, the accurate targeting of tumors anywhere in the body has become possible since several years. Current clinical applications manage to deliver a lethal dose of radiation to the cancerous region with an accuracy of about 2-3mm. Nevertheless, the tumour motion (induced by breathing, hearth beat or shifting of the patient) has to be compensated to be able to perform a precise irradiation. Conventional approaches are based on gating techniques, irradiation of tumour at specific phases of the respiration, or increasing of the target volume, until the complete tumour movement is covered.
An approach, developped in a collaboration of Prof. Schweikard and accuray Inc., Sunnyvale, CA, deals with this problem by tracking the motion of the patient's chest or abdomen using stereoscopic infrared camera systems. A mathematic model, the correlation model, can be computed based on the information of the external surrogates, which allows conclusions of the actual tumour movement. A robot based radiotherapy system, as e.g. the CyberKnife system, can use this information to compensate patient and respiration movements in real time.
Areas of Research:
Prediction of Breathing Motion:
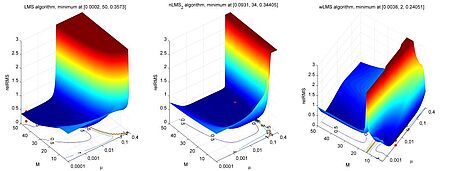
A new problem arising from this approach is the fact that neither the recording of the patient's position nor the repositioning of the robotic system is instantaneous. Currently employed systems exhibit delays between approximately 65 and 300 ms. This results in targeting errors of up to several millimeters. The systematic error can be reduced by time series prediction of the external surrogates. Beside the classical regression approaches, as e.g. the least mean square algorithm, current research focuses on machine learning approaches based on kernel methods and statistical learning. The continuous improvement of these algorithms is one main topic of this research project.
Camera setup to capture respiratory motion

In our lab, we also measure actual human respiration. To do so, 20 infrared LEDs were attached to the chest of a test person. These LEDs were subsequently tracked using a high-speed IR tracking system (atracsys accuTrack compact). To be able to accurately position the camera and to ensure camera stability, the camera was mounted on a robotic arm. A short sequence of the respiratory motion recorded can be seen in the following movie.

In our lab, we also measure actual human respiration. To do so, 20 infrared LEDs were attached to the chest of a test person. These LEDs were subsequently tracked using a high-speed IR tracking system (atracsys accuTrack compact). To be able to accurately position the camera and to ensure camera stability, the camera was mounted on a robotic arm. A short sequence of the respiratory motion recorded can be seen in the following movie.
Detection of Tumor Motion (Correlation Models):
Once the motion of the patient's chest is known, conclusions about the position of the tumor are drawn. This is done by using a correlation model mimicking the relation between surface motion and target motion. How this model is constructed and validated is also a matter of ongoing research.
Multivariate Motion Compensation:
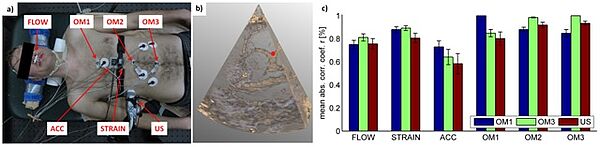
Current clinical praxis is the use of three optical infrared markers, which can be placed at any position of the chest or abdomen of the patient. As several studies have indicated, the correlation accuracy depends significantly on the marker placement and on the breathing characteristics of the patient. We investigate how this dependency can be reduced using multivariate measurement setups, e.g. acceleration, strain, air flow, surface electromyography (EMG). Aim of this research is the development of multi-modal prediction and correlation models. Special focus is placed on real time feature detection algorithms to detect the most relevant and least redundant sensors to increase the robustness of the complete system.
a) Sensor setup of a multivariate measurement with flow sensor (FLOW), optical marker 1-3 (OM 1-3), acceleration sensor (ACC), strain sensor (STRAIN) and ultrasound transducer (US),
b) Example of an ultrasound image and the selected target area (red dot) in the liver,
c) mean absolute correlation coefficients and standard deviation of all external sensors with respect to OM1, OM3 and US.
Probabilistic Motion Compensation:
Up to this point, surrogate based motion compensation requires a prediction and correlation model. The two models are used in sequence, meaning that the output of first model is used as the input to the second model (the order is arbitrary). Consequently, errors associated with the first model influence the result of the second model. In this context, Multi-Task Gaussian Process (MTGP) models have been investigated. These models offer for the first time the possibility to solve efficiently both problems and within one model. Studies have shown that this lead to a reduction of the total error. MTGP models are an extension of Gaussian Processes models, which are frequently used within the field of machine learning for regression tasks. The essential advantage of MTGPs is that multiple signals which are acquired at different sampling frequencies (even discrete time points) can be modelled simultaneously. The prediction accuracy is increased as the correlation between the signals is learned automatically.
MTGP Toolbox
The MTGP framework is very flexible and can be used for various biomedical problems as for instance the analysis of vital-sign data of intensive care unit patients. In cooperation with the Computational Health Informatics Lab (University of Oxford) a Matlab toolbox was developed. A detailed description of the toolbox and several illustrative examples can be found here. [Link Toolbox]
Publications
2012
Non-orthogonal Tool/Flange and Robot/World Calibration for Realistic Tracking Scenarios, International Journal of Medical Robotics and Computer Assisted Surgery , vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 407-420, 2012.
| DOI: | 10.1002/rcs.1427 |
| File: | rcs.1427 |
Evaluation of a wavelet-based least mean square motion prediction algorithm for lung and liver patients, Barcelona, Spain , 2012. pp. S12-S13.
| File: | ESTRO31.aspx |
Efficient SVR model update approaches for respiratory motion prediction, Düsseldorf, Germany , 2012.
Correlation between external and internal respiratory motion: a validation study, International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery , vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 483-492, 2012. Springer.
| DOI: | 10.1007/s11548-011-0653-6 |
| File: | s11548-011-0653-6 |
Evaluation of a wavelet-based least mean square algorithm for prediction of respiratory movements, Carlsbad, CA, USA , 2012. pp. accepted-for publication.
2011
High-accuracy ultrasound target localization for hand-eye calibration between optical tracking systems and three-dimensional ultrasound, Handels, Heinz and Ehrhardt, Jan and Deserno, Thomas M. and Meinzer, Hans-Peter and Tolxdorff, Thomas, Eds. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2011. pp. 179-183.
| DOI: | 10.1007/978-3-642-19335-4_38 |
| ISBN: | 978-3-642-19335-4 |
| File: | 978-3-642-19335-4_38 |
Real-time 4D ultrasound visualization with the Voreen framework, Vancouver, BC, Canada; New York, NY, USA: ACM, 2011. pp. 74:1.
| DOI: | 10.1145/2037715.2037798 |
| ISBN: | 978-1-4503-0971-4 |
| File: | 2037715.2037798 |
Performance Measures and Pre-Processing for Respiratory Motion Prediction, Vancouver, BC, Canada , 2011. pp. 3857.
| DOI: | 10.1118/1.3613523 |
| File: | 1.3613523 |
Predicting the Outcome of Respiratory Motion Prediction, Medical Physics , vol. 38, no. 10, pp. 5569-5582, 2011.
| DOI: | 10.1118/1.3633907 |
| File: | 1.3633907 |
Forecasting Pulsatory Motion for Non-invasive Cardiac Radiosurgery, International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery , vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 93-101, 2011.
| DOI: | 10.1007/s11548-010-0424-9 |
| File: | s11548-010-0424-9 |
Compensating for Quasi-periodic Motion in Robotic Radiosurgery., .... New York: Springer, 2011.
| DOI: | 10.1007/978-1-4614-1912-9 |
| ISBN: | 978-1-4614-1911-2 |
| File: | 978-1-4614-1912-9 |
Algorithms for Compensation of Quasi-periodic Motion in Robotic Radiosurgery, 2011.
| File: |
Adaptive Motion Compensation in Radiotherapy., .... Taylor Francis, 2011.
2010
A Novel Recording Tool for Education and Quality Assurance in Digital Angiography, Chicago, IL/USA , 2010.
Improving the Quality of Biomedical Signal Tracking using Prediction Algorithms, Coventry, United Kingdom; Coventry, UK , 2010. pp. 301-305.
| DOI: | 10.1049/ic.2010.0298 |
| ISBN: | 978-184600-0386 |
| File: | ic.2010.0298 |
Processing of Respiratory Motion Traces for Motion-Compensated Radiotherapy, Medical Physics , vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 282-294, 2010.
| DOI: | 10.1118/1.3271684 |
| File: | 1.3271684 |
Using ECG in Motion Prediction for Radiosurgery of the Beating Heart, Yang, Guang-Zhong and Darzi, Ara, Eds. The Royal Society, London , 2010. pp. 37-38.
| ISBN: | 978-0-9563776-1-6 |
2009
Motion Compensation in Radiosurgery, Lübeck, Germany: Institute for Robotics, University of Lübeck, 2009.
TH-C-304A-07: Real-Time Tracking of the Pulmonary Veins in 3D Ultrasound of the Beating Heart, Anaheim, CA, USA , 2009. pp. 2804.
| DOI: | 10.1118/1.3182643 |
| File: | 1.3182643 |
Prädiktion von Herzbewegungen, 2009.
Predicting Respiratory Motion Signals using Accurate Online Support Vector Regression (SVRpred), Berlin, Germany , 2009. pp. 255-256.
| DOI: | 10.1007/s11548-009-0340-z |
| File: | s11548-009-0340-z |
Liver Motion Tracking and Correlation to Surrogate Signals using 3D Ultrasound, 2009.

- Research
- Robotics Laboratory (RobLab)
- OLRIM
- MIRANA
- Robotik auf der digitalen Weide
- KRIBL
- Ultrasound Guided Radiation Therapy
- Digitaler Superzwilling: Projekt TWIN-WIN
- - Finished Projects -
- High-Accuracy Head Tracking
- Neurological Modelling
- Modelling of Cardiac Motion
- Motion Compensation in Radiotherapy
- Navigation and Visualisation in Endovascular Aortic Repair (Nav EVAR)
- Autonome Elektrofahrzeuge als urbane Lieferanten
- Goal-based Open ended Autonomous Learning
- Transcranial Electrical Stimulation
- Treatment Planning
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
- Navigation in Liver Surgery
- Stereotactic Micronavigation
- Surgical Microscope
- Interactive C-Arm
- OCT-based Neuro-Imaging
Floris Ernst

Gebäude 64
,
Raum 97
floris.ernst(at)uni-luebeck.de
+49 451 31015208
Ralf Bruder

Gebäude 64
,
Raum 92
ralf.bruder(at)uni-luebeck.de
+49 451 31015205